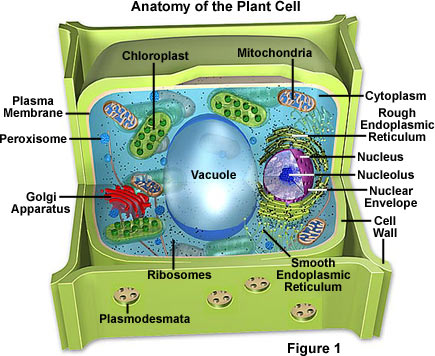
For example what around L'ville serves the same type of function as the nucleus? Is it different in animal vs plant cells? What about prokaryotes vs eukaryotes

We also talked about cell theory, which is? How was it discovered? Is it "proven" that all living things are made up of cells?
We also talked about why compartmentalization is important: cells need to have separate membrane bound structures (organelles) to do different functions at the same time (in which type of organism? Prok or Euk?).
What about specialization? allows different shapes/types of cells or organelles to have different functions that only they do
Size and shape - having different size and shape of cells allows for specialization and have their form 'match' their function.
See if you can identify examples of cells with each structure below: You can use the images below
High vs Low surface area
Block vs Web
Smooth vs Appendage
Connected vs Free
Motile vs Sessile
Sperm Cell
Cardiac Muscle
Neuron
Skin Cells
Blood Cells



No comments:
Post a Comment