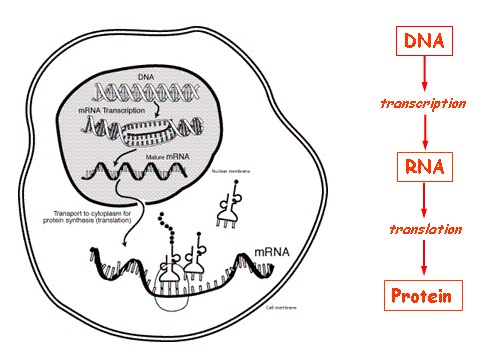
Remember DNA (a gene)--->mRNA--->Protein--->Trait. Where does environment come into play?
You then drew the process of translation up on the board. Here are the steps of translation: Make sure you can explain the whole process!
1. mRNA exits the nucleus
2. mRNA goes to the ribosome (in the cytoplasm) and ribosome attaches to the mRNA
3. mRNA moves through the ribosome 1 codon at a time
4. tRNA comes in and reads codon, if the anticodon is the correct one (with the complementary bases) the amino acid gets added to the peptide chain (remember the first codon read will always be the start codon... what amino acid does this code for?)
5. The amino acids are covalently bound to each other (this is called a peptide bond)
6. Once the ribosome gets to the stop codon of the mRNA, this is the signal to stop translation.
7. The protein (peptide chain) is released from the ribosomes and tRNA
8. The protein is then folded in a 3 dimensional structure.
Think about the following questions:
Describe the process of translation
How does translation relate to making proteins?
Where does translation take place?
What is the result of translation?
What do proteins do?
How does this relate to "Is Biology Destiny?"
Also here is the correct video for the HHMI video of translation
Can you transcribe then translate the following sequence?
TAC CCG GTA TTA CAG TGG GAA TGA ATT
You then drew the process of translation up on the board. Here are the steps of translation: Make sure you can explain the whole process!
1. mRNA exits the nucleus
2. mRNA goes to the ribosome (in the cytoplasm) and ribosome attaches to the mRNA
3. mRNA moves through the ribosome 1 codon at a time
4. tRNA comes in and reads codon, if the anticodon is the correct one (with the complementary bases) the amino acid gets added to the peptide chain (remember the first codon read will always be the start codon... what amino acid does this code for?)
5. The amino acids are covalently bound to each other (this is called a peptide bond)
6. Once the ribosome gets to the stop codon of the mRNA, this is the signal to stop translation.
7. The protein (peptide chain) is released from the ribosomes and tRNA
8. The protein is then folded in a 3 dimensional structure.
Think about the following questions:
Describe the process of translation
How does translation relate to making proteins?
Where does translation take place?
What is the result of translation?
What do proteins do?
How does this relate to "Is Biology Destiny?"
Also here is the correct video for the HHMI video of translation
Can you transcribe then translate the following sequence?
TAC CCG GTA TTA CAG TGG GAA TGA ATT