1. Independent Variable - juice type (orange, peach, grape, lemon).
2. Independent Variable - temperature (85, 60, 37, 24)
Part of your homework again tonight is to write up the PROCEDURE. You must have it written out when you arrive tomorrow.
Remember to use your original lab as a guide. You need to have a list of all the materials you need and then the steps (i.e. how to make the jello, how much to add to each tube, how many tubes does each group need). AND then a list of the IV, DEP, etc.
example from your original lab
1. Label test tubes as
“pineapple – hot,” “pineapple – RT,” “apple juice – hot,” “apple juice – RT,” and
“water.” Apply the tape at the top of
the test tube with a “tail” as shown at right, so steam from the water bath
does not remove the labels.
2. Prepare gelatin in
an appropriate beaker.
a.
Dissolve
the contents of a gelatin packet in ¼ cup cold water.
b.
Add
¾ cup boiling water to the mixture and stir until completely dissolved.
3. Pipette 3ml of
juice or water into each test tube according to the labels, using transfer
pipettes. Do not cross-contaminate
juices by using a pipette in different types of juice.
4. Place your “hot”
tubes in a beaker of water. Heat the
beaker on the hotplate until a thermometer in the water of the beaker reads 85°C. Carefully remove the tubes from the
heat. Allow contents to come to room
temperature (RT).
5. Add 10 ml ROOM
TEMPERATURE gelatin mixture to each test tube.
Use the big pipette for this and do not let the gelatin drip into the
green pipetter. Shake tubes well to
ensure mixing of contents
6. Refrigerate test
tubes overnight.
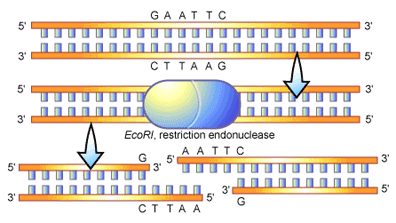
We also reviewed the sickle cell gel electrophoresis handout. If asked could you answer the following questions..
1. What is the phenotype if someone is Aa? Explain
2. What is a recessive allele?
3. How do we use restriction enzymes to determine genotype of sickle cell?
The last part of your homework is the handout below